
Why Residential Flat Roofing Deserves Your Attention
Residential flat roofing is a modern, efficient solution that combines unique aesthetics with practical benefits. While often associated with commercial buildings, these systems are increasingly popular for homes in Illinois, offering advantages from rooftop patios to easier solar panel installation. For homeowners considering their options, understanding the fundamentals of residential roofing is the first step.
Here’s what you need to know about flat roofs:
- Low-Slope Design: Flat roofs are not perfectly flat. They have a slight slope (at least 1/4 inch per foot) to ensure proper water drainage and prevent pooling.
- Main System Types: The three primary options are Built-Up Roofing (BUR), Modified Bitumen (MBR), and Single-Ply Membranes (EPDM, TPO, PVC).
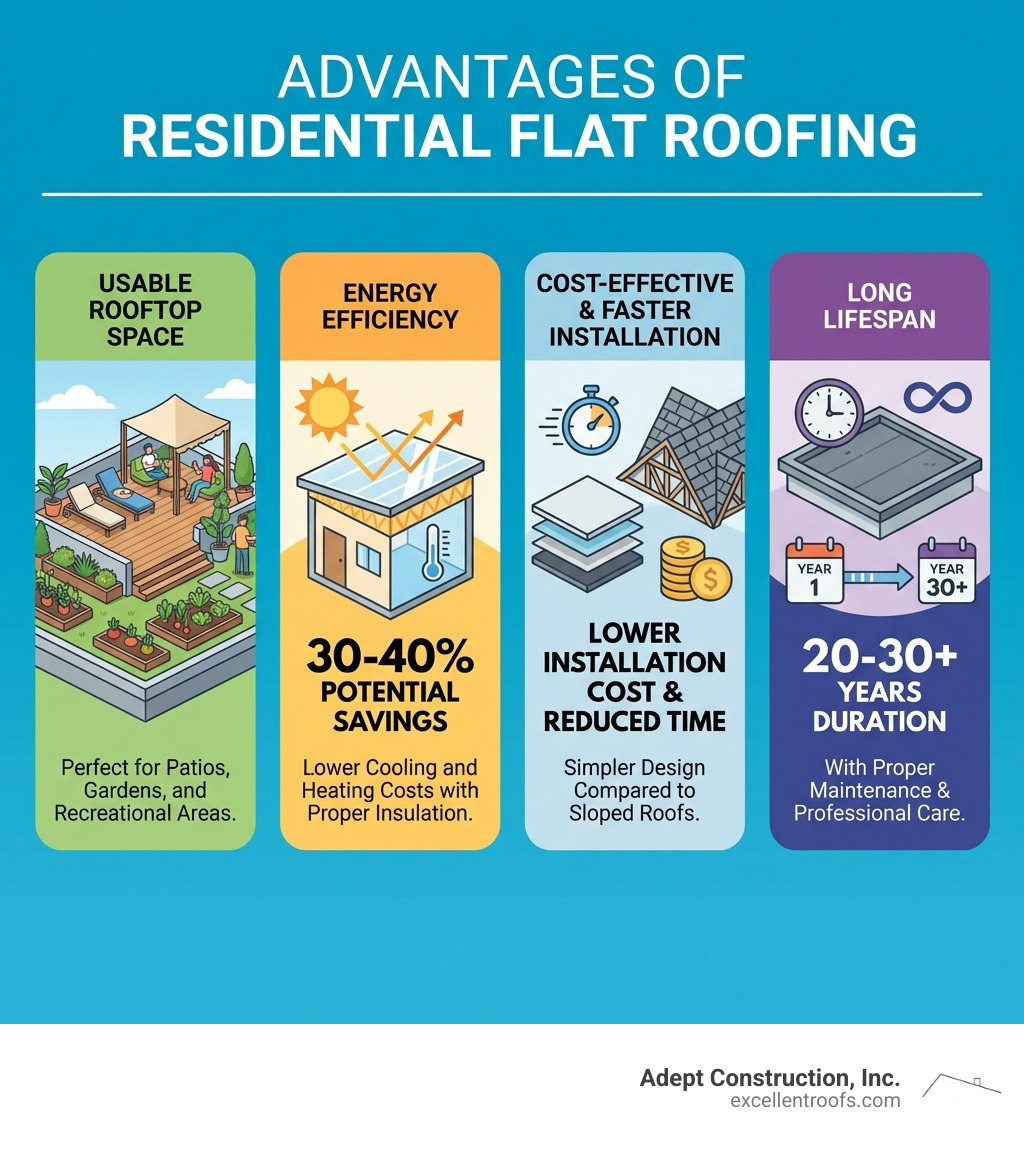
- Key Benefits: A professionally installed flat roof creates usable outdoor space, can improve energy efficiency by 30-40%, often costs less to install than pitched roofs, and can last 20-30+ years with proper care.
- Professional Installation is Crucial: The difference between a durable, energy-efficient asset and a leak-prone nightmare is proper material selection, drainage design, and expert installation.
With the right approach, a flat roof can serve your home reliably for decades, adding valuable functional space while reducing energy costs. Adept Construction has specialized in residential flat roofing installations and replacements across Chicago’s western suburbs since 1997, delivering superior workmanship that stands the test of time.
If you’re considering a flat roof for your home or need expert guidance on repair or replacement, we offer free estimates and transparent advice. Contact us today to discuss how a professionally installed flat roofing system can benefit your property.
Residential flat roofing terms to know:
Understanding the Fundamentals of Residential Flat Roofing
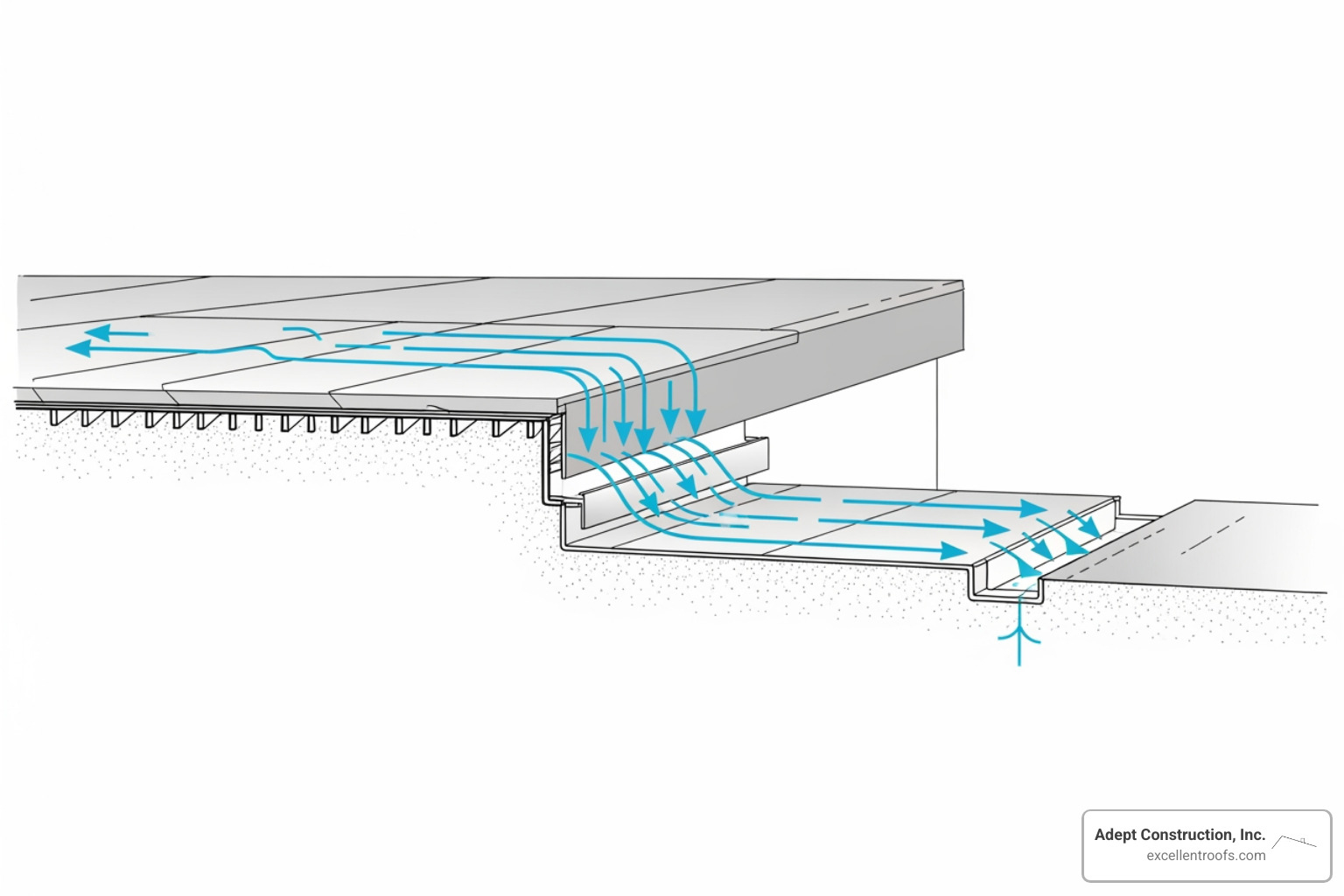
Flat roofs are engineered systems that require a slight slope to manage water effectively, a critical feature for longevity in Illinois’s climate of rain and snow. Without proper design, even the best materials can fail.
What is the Typical Slope of a Residential Flat Roof?
A residential flat roofing system is never perfectly level. It must have a low slope, typically a minimum of 1/4 inch per foot (a 2% grade), to direct water toward drainage points. This slight incline is essential to prevent “ponding”—standing water that can lead to leaks, structural damage, and premature material failure. A design fall of 1 in 40 is often recommended for optimal water shedding.
How Do Flat Roofs Drain Water Effectively?
An effective drainage system is the cornerstone of a healthy flat roof. The goal is to prevent water from sitting on the roof for more than 48 hours. Common drainage methods include:
- Internal Drains: Placed within the roof area, these connect to pipes that run through the building’s interior.
- Scuppers: These are openings in the roof’s edge or parapet wall that allow water to drain into external downspouts.
- Gutters and Downspouts: Similar to pitched roofs, gutters collect water along the roof’s perimeter and channel it away.
Main Components of a Flat Roof System
A durable residential flat roofing system is composed of several essential layers:
- Structural Deck: The foundation of the roof, usually made of plywood or OSB, which supports all other layers.
- Vapor Control Layer (VCL): Prevents moisture from inside the building from reaching the roof assembly and causing condensation.
- Insulation: Rigid boards that improve energy efficiency by reducing heat loss.
- Cover Board: A thin, rigid layer that provides a smooth, stable surface for the waterproof membrane.
- Waterproofing Membrane: The most critical layer, this impervious barrier (e.g., EPDM, TPO, PVC) protects the building from water.
- Flashing: Creates a watertight seal at all junctions, such as where the roof meets walls, chimneys, or vents.
Advantages, Drawbacks, and Myths
Residential flat roofing offers compelling benefits but also comes with common misconceptions.
- Advantages:
- Usable Space: Creates opportunities for rooftop patios, gardens, or green roofs.
- Easier Access: Simplifies maintenance for rooftop HVAC units and solar panels.
- Cost-Effective: Often faster and less expensive to install than complex pitched roofs.
- Energy Efficiency: Can provide 30-40% energy savings, especially with reflective “cool roof” materials.
- Drawbacks & Myths:
- Myth: They are completely flat. All flat roofs are sloped for drainage.
- Concern: Prone to leaks. Leaks are almost always due to poor installation or lack of maintenance, not an inherent flaw in the design.
- Risk: Water collection. While a low slope sheds water more slowly than a steep pitch, this risk is managed with proper drainage design.
A Deep Dive into Residential Flat Roofing Materials
Choosing the right material is the most critical decision for a flat roof, directly impacting its durability, cost, and lifespan. We help homeowners in Naperville, IL, and Downers Grove, IL, select the best fit for their property.

The Three Primary Types of Residential Flat Roofing Systems
Residential flat roofing materials fall into three main categories:
Built-Up Roofing (BUR): The traditional “tar and gravel” roof, BUR consists of alternating layers of bitumen (asphalt) and reinforcing fabrics. A top layer of gravel provides UV protection and durability. It is known for being a robust and affordable option, though the installation can be messy and odorous.
Modified Bitumen Roofing (MBR): An evolution of BUR, MBR is an asphalt-based material modified with polymers to improve flexibility and strength. This makes it highly puncture-resistant and able to withstand temperature fluctuations. It is typically installed in rolls and offers a great balance of performance and cost.
Single-Ply Membranes (EPDM, TPO, PVC): These modern systems consist of a single layer of synthetic material, offering a lightweight, flexible, and often energy-efficient solution.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): Often called “rubber roofing,” EPDM is a durable synthetic rubber known for its exceptional longevity (25-35+ years) and weather resistance. It is a cost-effective and proven material. If you’ve chosen Rubber Membrane Roofing (EPDM), keep an eye out for surface wear and tear.
- TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin): A popular white, reflective membrane prized for its energy efficiency. The light color reflects sunlight, lowering cooling costs. Its heat-welded seams create a strong, monolithic bond that is highly resistant to leaks.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Another thermoplastic membrane known for its robust durability, fire resistance, and chemical resistance. Like TPO, its heat-welded seams provide a superior watertight seal, making it a premium, long-lasting choice.
Here’s a quick comparison of these primary types:
| Feature | Built-Up Roofing (BUR) | Modified Bitumen (MBR) | EPDM (Rubber Membrane) | TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin) | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower to Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate to High | High |
| Lifespan | 20-30 years | 20-30 years | 25-35+ years | 20-30 years | 25-40+ years |
| Durability | Very Good | Excellent | Excellent | Very Good to Excellent | Excellent |
| Installation | Complex, Messy | Versatile | Relatively Easy | Relatively Easy | Relatively Easy |
| Energy Eff. | Low (dark surface) | Moderate | Low (dark, unless white) | High (reflective) | High (reflective) |
Can Shingles Be Used on a Flat Roof?
No. Standard roofing shingles are designed for sloped roofs and rely on gravity to shed water. Using them on a low-slope or residential flat roofing system will cause water to back up underneath them, leading to leaks, structural damage, and a voided manufacturer’s warranty. Specialized flat roofing materials are the only appropriate choice.
Key Considerations for Residential Flat Roofing Materials
When choosing a material, we guide clients to consider several key factors:
- Climate Suitability: Materials must handle Illinois’s hot summers and cold winters. Reflective TPO excels in heat, while EPDM offers superior flexibility in cold.
- Budget and Long-Term Value: We balance initial cost with lifespan, maintenance needs, and potential energy savings.
- Durability and Foot Traffic: If you plan to use the roof as a patio, the material must be robust enough to withstand traffic.
- Energy Efficiency Goals: For homeowners looking to reduce cooling costs, reflective “cool roof” options like white TPO or PVC are ideal.
- Aesthetics: The appearance matters, especially for visible roof sections or rooftop living spaces.
We often refer to our insights on Comparing Roof Materials: What’s Best for Your Climate? to help you make an informed decision.
Flat Roof Construction and Design Insights
The structural design and insulation strategy are as critical as the material choice for a residential flat roofing system, dictating its energy performance and moisture resistance.
What is the Difference Between a ‘Warm Roof’ and a ‘Cold Roof’?
The key difference is the placement of the insulation, which impacts energy efficiency and condensation risk.
Warm Roof: Insulation is placed above the structural roof deck, directly under the waterproof membrane. This keeps the entire roof structure warm, preventing condensation from forming within the assembly. A warm roof design offers superior thermal performance and is the strongly recommended method for climates like Illinois.
Cold Roof: Insulation is placed below the structural deck (between the joists). This leaves the deck cold and creates a risk of condensation, which can lead to rot and damage. Cold roofs require complex ventilation that is difficult to implement effectively and are generally not advised.
How Can a Flat Roof Be Used for Additional Space?
A major advantage of residential flat roofing is its potential to create valuable functional space. With proper structural support, a flat roof can become:
- A Rooftop Deck or Patio: An ideal platform for outdoor living and entertaining.
- A Green Roof or Garden: A beautiful, eco-friendly option that improves insulation and manages stormwater. Learn more from organizations like Green Roofs for Healthy Cities.
- A Platform for Solar Panels: The flat surface allows for optimal angling of solar panels to maximize energy generation.
Maintenance, Longevity, and Professional Installation
A residential flat roofing system requires proper care to deliver its full lifespan, which can easily exceed 20-30 years with professional installation and proactive maintenance.
Maintaining Your Residential Flat Roofing for Longevity
The key to a long-lasting flat roof is consistent maintenance. We recommend these steps:
- Inspect Regularly: Visually inspect your roof twice a year (spring and fall) and after major storms.
- Clear Debris: Keep the roof surface and drainage points (drains, scuppers) clear of leaves, branches, and other debris.
- Check for Ponding Water: Any water that remains on the roof for more than 48 hours indicates a drainage problem that needs to be addressed.
- Look for Damage: Scan the membrane for cracks, blisters, tears, or separating seams, especially around flashing.
- Address Issues Promptly: Contact a professional immediately if you notice any damage to prevent small issues from becoming major problems.
For a deeper look at our process, review our guide on What to Expect During a Roof Inspection.
Factors Influencing the Cost of a Flat Roof Replacement
The cost of a residential flat roofing replacement varies based on several factors:
- Roof Size and Complexity: Larger or more complex roofs require more materials and labor.
- Material Choice: Prices vary significantly between materials like BUR, MBR, EPDM, TPO, and PVC.
- Deck Condition: Repairing or replacing a rotted or damaged structural deck will add to the cost.
- Insulation Needs: Upgrading insulation to meet modern energy codes impacts the final price.
- Labor and Accessibility: Project complexity and roof accessibility affect labor costs.
For a detailed breakdown, consult our Roof Replacement Cost Complete Guide.
The Value of a Professional Contractor
Residential flat roofing is a specialized trade that demands professional expertise. Hiring a pro is essential for a successful, long-lasting installation.
- Expertise: Professionals understand the unique challenges of low-slope systems, ensuring proper drainage and seam integrity.
- Quality: We use high-quality materials and adhere to manufacturer specifications for a durable result.
- Warranties: A professional contractor provides workmanship warranties, protecting your investment.
- Peace of Mind: Hiring a licensed roofing contractor or inspector is crucial for a leak-free roof.
Whether you need a roof replacement in Downers Grove or a roof repair in Naperville, IL, choosing Adept Construction means investing in quality and durability.
Frequently Asked Questions about Residential Flat Roofing
Are flat roofs more energy-efficient than sloped roofs?
Yes, flat roofs can be more energy-efficient. This is due to the smaller attic space requiring less energy to heat and cool, and the ability to use reflective “cool roof” materials like white TPO or PVC. These surfaces reflect solar radiation, significantly reducing summer air conditioning costs and potentially leading to 30-40% energy savings.
How long does a residential flat roof last?
The lifespan of a residential flat roofing system depends on the material, installation quality, and maintenance. A well-maintained roof can last over 20 years. High-quality systems like EPDM and PVC can last over 30 years, while Modified Bitumen and BUR typically last 20-30 years. Regular inspections are key to maximizing longevity.
What are the main signs that a flat roof needs repair?
Early detection of damage is crucial. Key signs that your flat roof needs repair include:
- Ponding Water: Water that remains on the roof for more than 48 hours after rain is a critical sign of a drainage issue.
- Visible Damage: Look for cracks, blisters, tears, or punctures in the membrane.
- Separating Seams: Check for areas where seams are pulling apart or lifting.
- Interior Water Stains: Stains on ceilings or walls are a definitive sign of a leak.
If you notice any of these issues on your property in Downers Grove, IL or Naperville, IL, contact a professional for an inspection.
Your Partner for Expert Flat Roofing Solutions
Choosing the right flat roofing system is a significant investment in your home’s protection and value. From modern EPDM membranes to durable modified bitumen, the key to success is always professional installation and maintenance. At Adept Construction, Inc., our family-owned team has the specialized knowledge to guide you through every step, ensuring your residential flat roofing is built to last. For expert advice and a free, no-obligation estimate on your roofing project, contact our team today.




